How to Choose the Correct Compressor?
June 24, 2021
Air compressors are versatile machines and do various tasks when attached to pneumatic tools. Compared to electrical hand tools, as they have fewer moving parts, they produce more torque and power and are long lasting.
Need-To-Know When Selecting an Air Compressor
Compressors bring the air taken from outside to higher pressure levels and bring it into use. Although compressed air offers numerous advantages, it has high expenses. Due to the power used by the compressed air, it has high cost of electricity. In order to use the compressed air economically, it is required to choose a cost-effective and correct compressor.
Compressors are at the centre of many different applications, from small workshops to large industrial plants. Choosing the compressor that best fits the needs of your business or application can be confusing when you don't know which criteria to take into account. There are some tips we need to know to choose the most suitable compressor among piston, screw, frequency inverter and portable compressors.
There are some concepts that you should know when choosing compressors with high efficiency, resistance and air quality, and low carbon footprint. In this article, we will touch upon the issue of which criteria you should take into account when selecting the correct air compressor for your business. When selecting a compressor,
- Volumetric flow rate of air
- Operating pressure
- Compressor room dimensions
- Power consumption
- It is required to know the air quality.
Choosing a pressure compressor with higher values than your business needs is kind of like wasting your money. Amount of insufficient air or amount of air selected without foreseeing at least two years of growth capacity causes you to purchase a second compressor or to bear high investment costs by purchasing a large compressor that is far above the capacity. A quality and conformable compressor is the one that obtains the most efficient air by consuming minimum electrical energy according to conditions of use.
Piston compressors are suitable for the businesses that do not need continuous air at approximately 1 m³/min and below and up to 12 bar pressure. It is more economical to select the screw compressors for the businesses that need continuous air above 1 m³/min, up to 16 bar pressure.
Turbo compressors are advantageous in volumetric flow rate needs of 60 m3/min and above, where the screw compressors are insufficient. Multi-stage piston compressors for very high pressures and dynamic compressors for very high amounts of air can increase the efficiency of your business.
The power (kW) needed by the compressor in order to increase 1 m³/min of air to the desired pressure is called the specific energy consumption. By selecting the compressor with the lowest specific energy consumption (kW/m³), you can significantly reduce electrical energy consumption and operating costs. Similarly, while the compressor is running at idle (no-load), it should consume the least power.
No oil is required for some compressed air applications. In this case, it is obligatory to use oil-free piston compressors or oil-free screw type compressors.
What is Frequency Inverter (Converter)?
One of the issues we need to know once again when selecting a compressor is the frequency inverter, or in other words, the frequency converter. As the name indicates, frequency inverters are frequency converters. The frequency inverter used to control the engine revolutions converts an AC with a fixed mains frequency into a voltage with variable frequency (in both directions). Frequency inverters can energise a wide variety of equipment such as three-phase type motors, pumps and air conditioners. In three-phase type motors, the speed and torque of the AC motor can be controlled by changing the frequency. This control does not restrict the performance of a three-phase type motor, it just increases its efficiency. Such motors are often used in industrial environments.
How Does a Piston Compressor Work?

The piston compressor is the earliest and most common type of industrial compressor. It uses the displacement principle to increase the pressure of the enclosed gas or air volume. Piston compressors are available in various configurations, including single-stage, two-stage, lubricated or oil-free. Most piston compressors have self-propelled valves that open and close depending on the pressure differences on either side of the valve disc. Some larger machines are equipped with a crosshead, gaskets and a ventilated spacer to prevent oil from transferring to the compression room.
In a piston compressor with a valve system and two stainless steel valve discs, the piston moves downwards and draws air to the cylinder. The largest disc bends and folds downwards, allowing air to pass through. When the piston moves upwards, the large disc flexes again to seal against the valve seat. Compressed air is then forced through the hole in the valve seat and delivered to the after-treatment.
What is the Difference of the Screw Compressor?
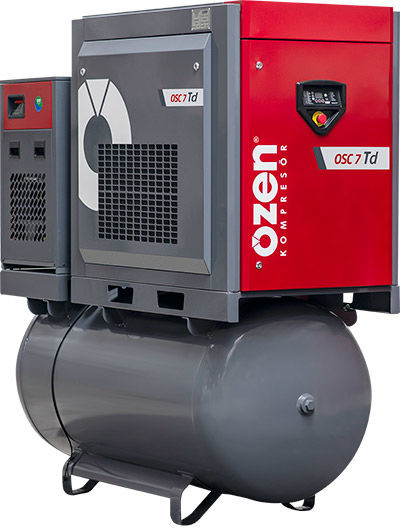


Unlike piston compressors, screw compressors have no valves or other mechanical forces that can cause unbalance. This combines a large flow rate with small external dimensions while allowing the screw compressor to operate at high speeds. It has two main versions, including oil-free and oil-injected, with the options of constant-speed or variable-speed driver process. The actual benefit of the screw compressors is its energy efficiency.
Where is the Portable Compressor Used?

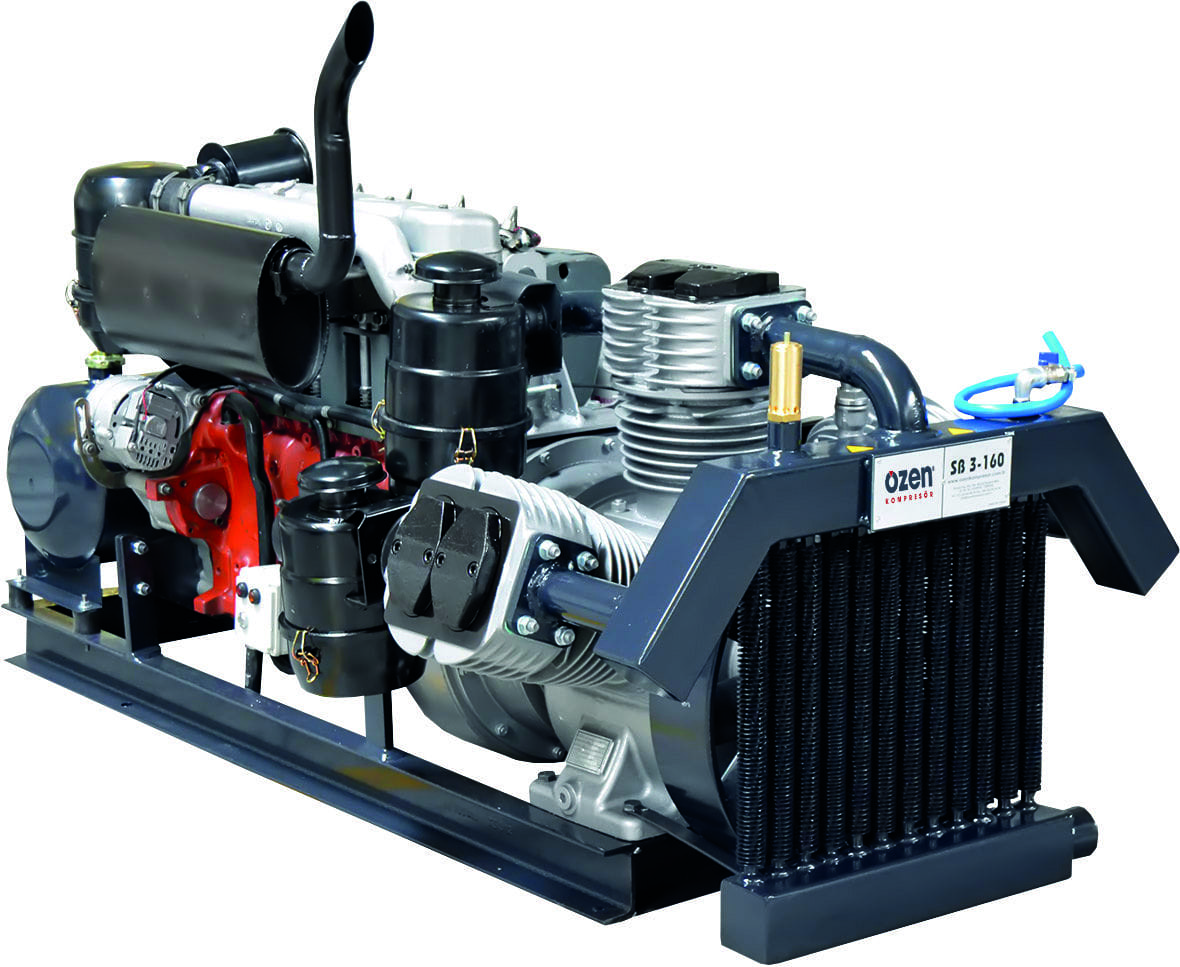
Portable compressors are used in many applications, from building works and road repair to rescue operations. Portable compressors have usage areas such as oil-injected screw compressors powered by diesel engines, diesel-engine bulk trailer compressors and mobile piston compressors for use in off-road drilling works at building sites as well as road repair, pipeline works, rock strengthening, sandblasting, rescue operations etc. Very small and very large portable compressors are sometimes also offered with electric engines.
